The Internet of Things (IoT) has penetrated our lives in multiple ways. Some incarnations of these IoT systems are Smart Homes, Connected Cars, Smart Factories, and Smart Grids that consolidate/manage office data.
In all these use cases, an IoT cloud architecture is introduced when there is a need to process and analyse large data sets.
The exceptional opportunities that cloud computing promises, have encouraged organisations to seek implementation of this service in their business operations. However, the vast number of devices and conditions to be satisfied to make IoT work, may be a deterrent in many cases. This is where the services of a reliable full-stack IoT solutions provider can prove to be invaluable.
To achieve the expected results, the IoT cloud platform should be robust, scalable and agile with impeccable security features. The components of the cloud architecture should also work together seamlessly.
Here we explore the various aspects of IoT cloud architecture, with special focus on the database design factors.
Layers of Cloud Architecture for IoT
In an IoT cloud architecture, the data flows across many layers. Although the actual cloud platform configuration may differ between organisations, all these solutions accomplish the same basic objective.
This encompasses allowing different devices to connect to the network, processing the data and utilizing the insights gained for automation. A significant part of the data processing takes place in the cloud databases and reporting layer.
Let us take a look at the basic components of an IoT architecture.
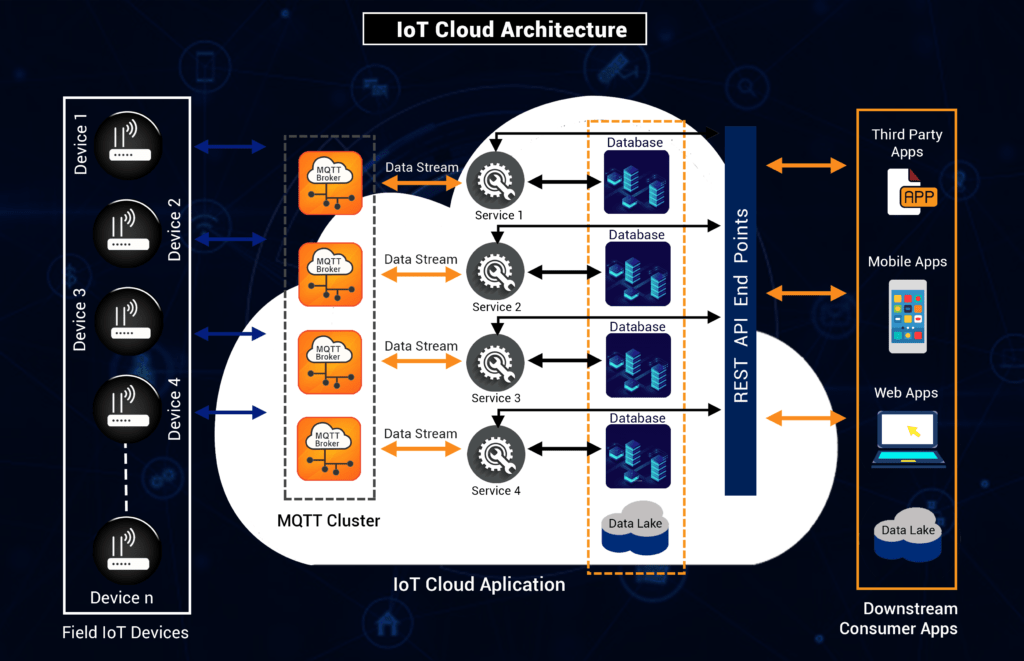
- IoT Devices
- IoT Integration Middleware
- Cloud Servers
- Databases
- Downstream Applications/BI Tools
The device integrates with sensors or actuators and establish a connection with the IoT Integration Middleware. In some use cases, multiple devices may be grouped together and connected to an IoT gateway infrastructure that transmits device data to the IoT Integration Middleware. The devices have drivers, i.e., software that enables access to the sensors/actuators.
The IoT Integration Middleware is an integration layer for various devices when connecting with the cloud. It receives data from the connected devices, processes it and transmits this information to downstream applications. The processing of data may include the evaluation of condition-action rules, and deployment of commands to the device sensors based on the evaluation.
If the device supports a suitable communication technology (WiFi or IP over Ethernet), a transport protocol such as MQTT or HTTP and a compatible payload format, it can transmit data directly to the Integration Middleware. Otherwise, an IoT gateway has to be installed in between for communication with the middleware platform.
The middleware broker also ensures that there is no loss of data, since asynchronous communication is established with the connected device.
Servers are the most important part of the IoT cloud, as these are needed for providing business services to customers. These are virtual machines linked to individual databases.
Based on the business requirements for data storage and processing, SQL and No SQL databases can be configured on the IoT cloud. SQL databases store data in the form of two-dimensional tables. The main disadvantage of this kind of database is its performance. No SQL databases are much more efficient and real-time.
The cloud servers are connected to third-party apps, mobile/web applications or business intelligence tools through REST API endpoints.
When a large number of IoT devices and applications are connected to the IoT cloud platform, the cloud application servers will have to transfer a huge amount of data. In order to streamline this, load balancing is enforced. This ensures even distribution of workload across the backend servers and improves efficiency.
IoT Cloud Architecture – Database Design Best Practices
While designing the database for an IoT cloud, there are several points to be considered. An experienced IoT cloud architecture development company can help you identify the right kind of database for a specific business use case.
Some technical aspects of designing a cloud database are given below.
- Questions to be asked while determining the type of database for a cloud architecture are:
- Is the consistency of data important for the implementation?
- Is high availability of data a crucial aspect of the project?
- In case of downtime in data availability, would there be serious repercussions?
If there is a requirement to handle a large amount of data, No SQL database can be utilized.
- Another point to be considered when selecting No SQL database is the type of analysis that will be performed with the data.
- Are we dynamically generating reports from the data/insights?
- Is there a need to perform time-series analysis of data?
Sometimes, the data collected is integrated with a Business Intelligence tool for generating insights. In this case, the data can be stored in a cloud database or data lake, and an API can be developed for the BI tool to access the data.
- At the time of database design, the assessment of value of data should not be missed. For instance, on a telematics platform, accidental alert is critical information. It is important that a reliable protocol is used for communication between the device and the cloud platform to ensure there is no data loss. The asynchronous communication between the devices and cloud servers can be managed efficiently by deploying an MQTT Cluster.
- Scalability of the IoT cloud platform should also be taken into account when designing the No SQL database. If there is an unprecedented need to integrate a large number of devices in the future, the cloud solution should be able to handle it. Hence, this should be a point in the checklist in the database design phase itself.
- Optimization is another aspect to be considered while selecting the cloud database. It is crucial to determine the amount of time the data needs to be stored.
- Is it necessary to store the data for an extended period of time?
- Does the business requirement include storage of both data and insights?
Let us examine this in detail. In some use cases, the data collected throughout a couple months can be stored in an SQL database if only the reporting aspect is required. Once the reports are generated, the data can be deleted.
An example of this is predictive maintenance. In such a setup, there is a need to perform time-series analysis of data. The system collects the health information of the monitored devices on a periodic basis. There will be a large amount of data collected this way. If this information is stored for a year or so and then time-series analysis is performed, it is possible to generate some insights. Following this, the data can be discarded.
Likewise, there are also use cases where there is no need to store the data beyond a short period of time. For example, if we are tracking the location of a device for 5 days, we can reduce the load on the database by automatically deleting the data after the stipulated time period.
The aforementioned principles will help in optimizing database design and reducing overall cost of the solution.
Conclusion
The use cases covered by IoT will span across commercial, domestic, healthcare and industrial contexts in the future.
While designing a robust IoT infrastructure, it is crucial to lay a lot of emphasis on the IoT cloud architecture and cloud database design. The points mentioned in this article will provide a base for understanding the design requirements of IoT cloud databases. This also helps in mitigating design flaws that may be expensive to resolve in the future.


